Temperature dependence of the hydrogen bond network in trimethylamine N-oxide and guanidine hydrochloride–water solutions
Abstract
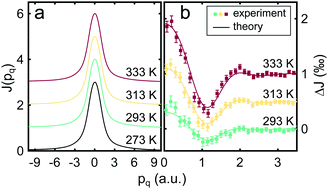
We present an X-ray Compton scattering study on aqueous trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) and guanidine hydrochloride solutions (GdnHCl) as a function of temperature. Independent from the concentration of the solvent, Compton profiles almost resemble results for liquid water as a function of temperature. However, the number of hydrogen bonds per water molecule extracted from the Compton profiles suggests a decrease of hydrogen bonds with rising temperature for all studied samples, and the differences between water and the solutions are weak. Nevertheless, the data indicate a reduced bond weakening with rising TMAO concentration up to 5 M of 7.2% compared to 8% for pure water. In contrast, the addition of GdnHCl appears to behave differently for concentrations up to 3.1 M with a weaker impact on the temperature response of the hydrogen bond structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...