Solid electrolyte interphase formation by propylene carbonate reduction for lithium anode
Abstract
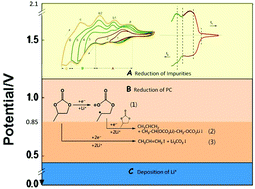
The naturally formed solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) of lithium (Li) with organic electrolytes is fragile and can result in repeated exposure of fresh Li metal to the electrolyte during plating/stripping cycles. Building an artificial SEI layer is an effective way to enhance its stability and improve the electrochemical deposition behavior of Li. Using non-Li metal substrate to construct Li metal electrode is a more applicable method than using direct Li metal anode. In this study, the possibility of electrochemical reduction of propylene carbonate (PC) as an artificial SEI formation reaction for Li metal anode was evaluated. The results show that PC reduction can be divided into two stages: in the potential region higher than 0.85 V (vs. Li/Li+), the soluble free radical anion CH3–ĊH–CH2–OCO2− is formed and can be re-oxidized. In the potential region between 0.85 and 0.55 V (vs. Li/Li+), the insoluble reduction products CH3CH(–OCO2Li)CH2–OCO2Li and Li2CO3 are formed and construct the SEI film. By controlling the PC reduction rate with limited current, the morphology and construction of the SEI film could be improved, and thus the Li plating/stripping cycling efficiency could be enhanced. This can be considered a fundamental concept for high quality artificial SEI formation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...