Rate constants, processivity, and productive binding ratio of chitinase A revealed by single-molecule analysis
Abstract
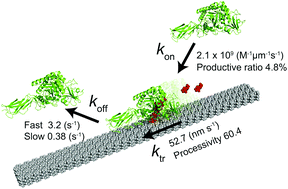
Serratia marcescens chitinase A is a linear molecular motor that hydrolyses crystalline chitin in a processive manner. Here, we quantitatively determined the rate constants of elementary reaction steps, including binding (kon), translational movement (ktr), and dissociation (koff) with single-molecule fluorescence imaging. The kon for a single chitin microfibril was 2.1 × 109 M−1 μm−1 s−1. The koff showed two components, kfastoff (3.2 s−1, 78%) and kslowoff (0.38 s−1, 22%), corresponding to bindings to different crystal surfaces. From the kon, kfastoff, kslowoff and ratio of fast and slow dissociations, dissociation constants for low and high affinity sites were estimated as 2.0 × 10−9 M μm and 8.1 × 10−10 M μm, respectively. The ktr was 52.5 nm s−1, and processivity was estimated as 60.4. The apparent inconsistency between high turnover (52.5 s−1) calculated from ktr and biochemically determined low kcat (2.6 s−1) is explained by a low ratio (4.8%) of productive enzymes on the chitin surface (52.5 s−1 × 0.048 = 2.5 s−1). Our results highlight the importance of single-molecule analysis in understanding the mechanism of enzymes acting on a solid–liquid interface.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Complex molecular systems: supramolecules, biomolecules and interfaces


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...