Unexpected formation of scheelite-structured Ca1−xCdxWO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) continuous solid solutions with tunable photoluminescent and electronic properties
Abstract
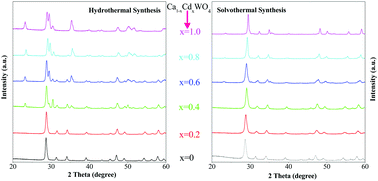
Design of a solid solution with tunable functionality is an attractive strategy toward realizing novel devices with multi-functionalities. In this work, a series of Ca1−xCdxWO4 solid solutions in the entire range 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 with tetragonal scheelite structure have been successfully prepared for the first time. X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) and Fourier transform Raman (FT-Raman) spectroscopies indicated that all the nanocrystals have a tetragonal scheelite structure without wolframite phase. Structural refinement data revealed that the lattice volume decreased with the replacement of Ca2+ by Cd2+ ions. UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra indicated that optical band gap reduced with the replacement of Ca2+ by Cd2+ ions. Scanning electron microscopic (SEM) images showed that morphologies of the nanocrystals changed with the chemical compositions. The structure evolution of the solid solutions was further investigated by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). Moreover, the influence of chemical compositions on the photoluminescent and electric performance has been performed and discussed. The reported synthetic approach and findings reported here are important to understand the structure and structure–property relation of scheelite-structured tungstate and molybdate compounds, which has potential applications in the design of other kinds of novel functional materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...