Optimal hydrogen storage in sodium substituted lithium fullerides
Abstract
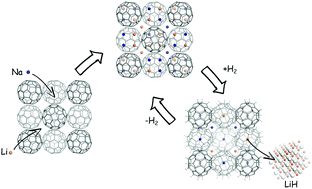
Through the substitution of Li with Na in Li6C60, we synthesized a series of mixed alkali cluster intercalated fullerides, NaxLi6−xC60. These compounds share lattices of Na6C60 and Li6C60 with a cubic parameter linearly dependent on x. H2 absorption and desorption were studied by means of charge/discharge kinetic measurements and coupled calorimetric–manometric evaluation. By varying the stoichiometry, we found the best compromise among the absorption rate, temperature and amount of hydrogen for x = 0.5 and 1. Small concentrations of Na substituted to Li significantly lower the absorption temperature of Li6C60, improving the hydrogenation capacity, the kinetics, and the dehydrogenation enthalpy, the latter being 43.8 kJ mol−1 H2 for x = 1. This study moves further toward the utilization of intercalated fullerides for hydrogen storage applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...