Electrochemical estimation of the active site density on metal-free nitrogen-doped carbon using catechol as an adsorbate†
Abstract
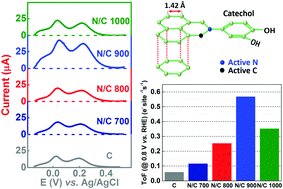
Carbon is heat-treated with a nitrogen-containing precursor (ammonia) to obtain nitrogen-doped carbon and the composition is estimated using CHN and XPS analysis. The active site density of the carbon and nitrogen-doped carbon is quantified using 1,2-dihydroxybenzene (catechol) molecules as an adsorbate in phosphate buffer (pH 7) solution. The features of the voltammograms of the catechol-adsorbed high surface area carbon and nitrogen-doped carbon are similar to that of the polished nitrogen-grafted glassy carbon electrode (GCE) reported in the literature. At the same time, the polished GCE does not show any well-defined catechol adsorption features. It is found that the adsorption charge (obtained by integrating the peak area, after subtracting the background) is in the order of N/C 900 > N/C 1000 > N/C 800 > N/C 700 > C. A similar trend is observed in their oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity in 0.1 M KOH. Moreover, the turnover frequency (ToF) of the catalysts is calculated and it is comparable to that reported in the literature using other methods for non-precious catalysts. Therefore, the adsorption charge can be correlated with the active site density of the carbon and nitrogen-doped carbon samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...