Concerted double proton-transfer electron-transfer between catechol and superoxide radical anion†
Abstract
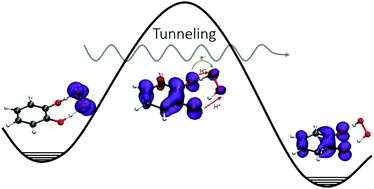
We have carried out a computational study on the reactivity of catechol (1,2-dihydroxybenzene) towards superoxide radical anion (O2˙−) in water, N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), pentyl ethanoate (PEA) and vacuum using density functional theory and the coupled cluster method. Five reaction mechanisms were studied: (i) sequential proton transfer followed by hydrogen atom transfer (PT-HT), (ii) sequential hydrogen atom transfer followed by proton transfer (HT-PT), (iii) single electron transfer (SET), (iv) radical adduct formation (RAF) and (v) concerted double proton-transfer electron-transfer (denoted as global reaction, GR). Our results show that catechol and superoxide do not react via a sequential reaction mechanism (initial PT, initial HAT or SET). Instead, the reaction proceeds via a concerted double proton-transfer electron-transfer mechanism yielding hydrogen peroxide and catechol radical anion. The protons are transferred asynchronously between the σ orbitals of the catechol oxygen atoms to superoxide, while the electron is transferred between oxygen π orbitals in the same direction. The calculated rate constants in aqueous media agree with the experimental values reported in the literature. This suggests that the mechanism proposed in this work is adequate to describe this reaction. In addition, our results show that the reaction exhibits a large tunneling effect.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...