The formation mechanism of the initial C–C chain in ethanol synthesis on γ-AlOOH(100)†
Abstract
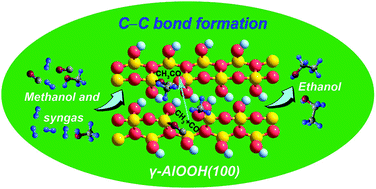
An in-depth understanding of the reaction mechanism at the molecular level is the key to guide the synthesis of ethanol over the CuZnAl catalyst, which is one of the major challenges for ethanol application in energy. Reported herein is a density functional theory study of ethanol synthesis from mixed methanol and syngas on the γ-AlOOH(100) surface. The possible elementary reactions are unambiguously identified and for the first time we confirm the high reactivity of the γ-AlOOH(100) surface for the initial C–C chain formation via CO insertion into CH3, which has a 62.8 kJ mol−1 (0.65 eV) activation barrier that is significantly lower than the barriers previously reported. And its corresponding reaction energy is −288.2 kJ mol−1 (−2.99 eV). Bader charge analyses indicate that it is advantageous for the nucleophilic attack of CO to the neighboring CH3 on the γ-AlOOH(100) surface. Our calculations show that ethanol synthesis starts with CH3OH dissociation, goes through CH3O dissociation to yield CH3, subsequently, CO inserts into CH3 to form CH3CO, which is further hydrogenated to yield CH3CHO and eventually obtain C2H5OH. And the formation of intermediate CH3 is the rate-determining step of the overall reaction. The results not only provide new mechanistic insights into the role of γ-AlOOH but also may be useful for the rational designing and optimizing of the CuZnAl catalyst for ethanol synthesis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...