Single-molecule probing of amyloid nano-ensembles using the polymer nanoarray approach†
Abstract
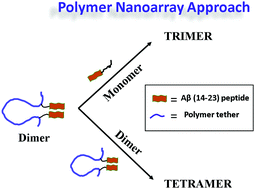
Soluble amyloid-beta (Aβ) oligomers are the prime causative agents of cognitive deficits during early stages of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The transient nature of the oligomers makes them difficult to characterize by traditional techniques, suggesting that advanced approaches are necessary. Previously developed fluorescence-based tethered approach for probing intermolecular interactions (TAPIN) and AFM-based single-molecule force spectroscopy are capable of probing dimers of Aβ peptides. In this paper, a novel polymer nanoarray approach to probe trimers and tetramers formed by the Aβ(14–23) segment of Aβ protein at the single-molecule level is applied. By using this approach combined with TAPIN and AFM force spectroscopy, the impact of pH on the assembly of these oligomers was characterized. Experimental results reveal that pH affects the oligomer assembly process. At neutral pH, trimers and tetramers assemble into structures with a similar stability, while at acidic conditions (pH 3.7), the oligomers adopt a set of structures with different lifetimes and strengths. Models for the assembly of Aβ(14–23) trimers and tetramers based on the results obtained is proposed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...