Anchoring ceria nanoparticles on graphene oxide and their radical scavenge properties under gamma irradiation environment†
Abstract
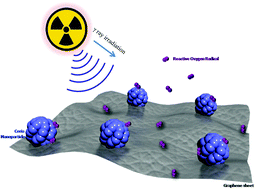
Polymer networks such as those of epoxy resin, as common protection materials, possess radiolytic oxidation degradation effects under gamma irradiation environment, which have a great accelerating effect on the ageing rate and severely limit their potential applications for metal protection in the nuclear industry. To overcome this, we report a simple scheme of anchoring crystalline ceria nanoparticles onto graphene sheets (CG) and incorporate it into the epoxy resin, followed by thermal polymerization to obtain CeO2/graphene-epoxy nanocomposite coating (CGNS). We had proven that graphene might act as “interwalls” in the epoxy matrix, which will result in space location-obstruct effect as well as absorb the radicals induced by γ-ray irradiation. Moreover, owing to the interconversion of cerium ions between their +3 and +4 states coupled with the formation of oxygen vacancy defects, electron spin resonance (ESR) detection shows that CeO2/graphene (CG) could act as a preferable radical scavenger and achieve better performance in trapping radicals than single graphene based composite. Electrochemical data strongly demonstrate that CeO2/graphene is capable of maintaining the anti-corrosion properties under gamma irradiation environment. Therefore, the designed hybrid CeO2/graphene-epoxy composite can be considered as potential candidates for protective coatings in nuclear industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...