Zipf's law for pore ranking and pore anisotropy†
Abstract
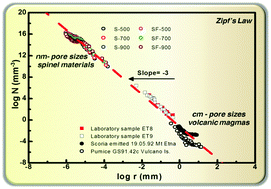
In this work it is shown that the range of Zipf's law for the ranking of random pores in solids upholds for ∼10 orders of magnitude, from nm pore sizes in laboratory-made materials, to cm pore sizes occurring in solidified volcanic magmas. Also it is demonstrated that for MCM-type materials with organized mesopores, the out-of-trend data in the Zipf plots, corresponding to the sudden pore filling during N2 adsorption, can be used for the convenient estimation of local pore anisotropy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...