Identification of the protonation site of gaseous triglycine: the cis-peptide bond conformation as the global minimum†
Abstract
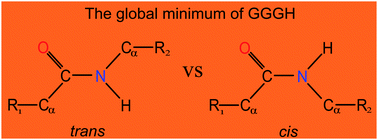
Extensive ab initio investigations have been performed to characterize stable conformers of protonated triglycine (GGGH) in the gas phase. Calculations using the composite CBS-QB3 method confirmed that the most favorable site of protonation on triglycine at 298 K is still the traditional amino nitrogen, rather than the more-recently reported amide oxygen. Furthermore, a non-proline cis-peptide bond conformer is identified for the first time as the global minimum of GGGH. Further transition state calculations considering the temperature effects explained why the previous experimental infrared multiple photon dissociation (IRMPD) spectrum contains a combination of two local minima, rather than a global one. First-principles simulations have been performed for near-edge X-ray absorption fine-structure (NEXAFS) spectra and X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) at the C, N and O K-edges to identify the notable spectral differences that enable the unambiguous identification of different protonated forms. The calculated proton affinity (PA) and gas basicity (GB) of triglycine are in excellent agreement with the experimental values. Our study thus provides valuable insights into the protonation of short peptides and illustrates the competition between cis and trans peptide bonds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...