Computational analysis of site differences in selective aliphatic C–H hydroxylation by nonheme iron–oxo complexes†
Abstract
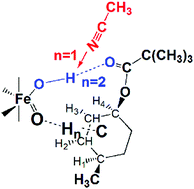
Selective C–H hydroxylation by nonheme iron complexes offers a promising method in the field of organic synthesis. Aliphatic C–H bond oxidation reactions of pivalate (R) catalyzed by [Fe(S,S-PDP)(CH3CN)2]2+ (CAT1) were examined using the density functional theory. Our calculations of the CH3CN solvent agree with the experimental findings. However, it was observed that the gas-phase results did not replicate selective C–H hydroxylation observed experimentally when CAT1 catalyzed hydrocarbon oxidations by H2O2via an HO–FeV![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O oxidant (CAT1a). We inferred that the difference was mainly from hydrogen bonding formation, (CAT1a) O–H⋯O
O oxidant (CAT1a). We inferred that the difference was mainly from hydrogen bonding formation, (CAT1a) O–H⋯O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C (R), in certain gaseous H-abstraction transition states (TSH). Then, the appearance of the stronger (CAT1a) O–H⋯N
C (R), in certain gaseous H-abstraction transition states (TSH). Then, the appearance of the stronger (CAT1a) O–H⋯N![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CCH3-solvent weakened the aforementioned interaction, leading to C–H activation influenced primarily by their electronic and steric properties. Such a deduction explained the same selective C–H found in both phases of reactions with CAT1b, a cyclic ferric peracetate oxidant, by the reason of TSH without the influence of H-bonding. Another interesting finding was that the commonly recognized radical intermediate was further isomerized by a favorable electron rearrangement. Thus, the subsequent OH-rebound behavior proceeded by an electrostatic interaction. This study provides mechanistic clues for modifying regioselective C–H hydroxylation for molecule synthesis applications.
CCH3-solvent weakened the aforementioned interaction, leading to C–H activation influenced primarily by their electronic and steric properties. Such a deduction explained the same selective C–H found in both phases of reactions with CAT1b, a cyclic ferric peracetate oxidant, by the reason of TSH without the influence of H-bonding. Another interesting finding was that the commonly recognized radical intermediate was further isomerized by a favorable electron rearrangement. Thus, the subsequent OH-rebound behavior proceeded by an electrostatic interaction. This study provides mechanistic clues for modifying regioselective C–H hydroxylation for molecule synthesis applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...