Coexistence of ice clusters and liquid-like water clusters on the Ru(0001) surface
Abstract
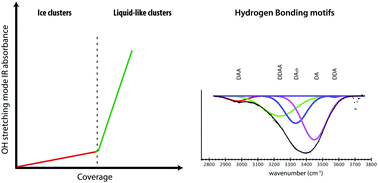
The RAIRS spectra of water adsorbed on Ru(0001) at 85 K are recorded from 600 cm−1 to 4000 cm−1. Measured at water coverages from 0.13 ML to 2.0 ML, the RAIRS spectra suggest that chemisorption of water on Ru(0001) depends on coverage. Water adsorbs on a clean Ru surface as chemisorbed ice-like clusters (likely through an O–Ru bond) up to 0.33 ML. Above this coverage, the chemisorbed layer saturates. Upon more exposure, water adsorbs as a liquid-like H-bonded layer without bonding to the Ru substrate. The chemisorbed water absorbs 7 times less IR per molecule than the liquid-like structure, which indicates that the orientation of the chemisorbed water is more parallel to the surface. Additionally, the influence of water–Ru bonding on H-bonding is reflected in the OH symmetric stretching mode. Under perturbation from water–Ru bonding, a large red shift (40 cm−1) in the free OH stretching frequency is observed in the chemisorbed clusters. By deconvoluting the main H-bonded OH stretching peak into five Gaussian sub-bands at 2945 ± 5 cm−1, 3210 ± 5 cm−1, 3300 ± 15 cm−1, 3430 ± 5 cm−1 and 3570 ± 10 cm−1, changes in the H-bonding network are rationalized in terms of H-bonding motifs. The donor–acceptor–acceptor motif is significant only in the chemisorbed clusters. On the other hand, the donor–acceptor motif dominates in the liquid-like structure, which increases the disorder present in the adlayer. Although chemisorption is suppressed above 0.33 ML, no structural changes in the ice-like clusters are observed up to multilayer coverage. Therefore, ice-like and liquid-like water coexist in a meta-stable state at 85 K.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...