Infrared dynamics study of thermally treated perfluoroimide acid proton exchange membranes
Abstract
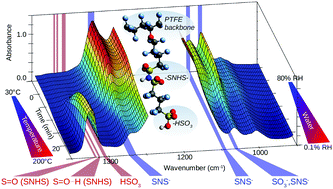
The temperature induced dehydration process of the 3M Brand perfluoroimide acid (PFIA), an advanced proton exchange membrane for fuel cells, was studied by in situ infrared spectroscopy to understand proton transport processes under conditions of low hydration levels. A comprehensive assignment of the vibrational bands of PFIA in the mid infrared region is provided. Investigation of the kinetics in conjunction with 2D correlation spectroscopy methods revealed the sequential process of the hydration and dehydration in a conclusive model. The results indicate that at a lower water content the sulfonate group of the PFIA side chain is preferentially ionised and involved in a hydrogen bonding structure with the sulfonyl imide acid group, until a sufficient amount of water is present to ionise the second ionic site. Comparison to the well-understood NAFION™ membrane revealed that under low humidity conditions a higher amount of water is retained in PFIA in a state most similar to liquid water. The results contribute to a better understanding of water retention capability and thus proton conductivity under high-temperature and low-humidity conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...