Recurrent supramolecular scenarios within complex 3-D hydrogen bond networks derived from organic ammonium salts of (4-amino-1-hydroxybutylidine)-1,1-bisphosphonic acid†
Abstract
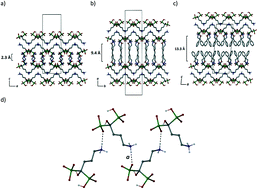
Reactions of (4-amino-1-hydroxybutylidine)-1,1-bisphosphonic acid (alendronic acid = LH5) with organic amines or diamines in a 1 : 2 or 1 : 1 ratio in aqueous solution gave a range of nine new compounds of the general formula [(RN)H]2[LH3] or [(R′N)H2][LH3]. Crystal structures are reported for: (i) [enH2][LH3]·2(H2O) 1; (ii) [MeenH2][LH3]·3(H2O) 2; (iii) [Me2enH2][LH3]·3.5(H2O) 3; (iv) [Et2enH2][LH3]·2(H2O) 4; (v) [cdaH2][LH3]·3(H2O) 5; (vi) [xdaH2][LH3]·4(H2O) 6; (vii) [odaH2][LH3]·2(H2O)·0.5(EtOH) 7; (viii) [PheaH]2[LH3]·2(H2O) 8; (ix) [melH]2[LH3]·7(H2O) 9 (en = H2N(CH2)2NH2; Meen = Me(H)N(CH2)2NH2; Me2en = Me(H)N(CH2)2N(H)Me; Et2en = Et2N(CH2)2NH2; cda = trans-rac-1,2-C6H10(NH2)2; xda = m-C6H4(NH2)2; oda = H2N(CH2)8NH2; Phea = 2-Ph(CH2)2NH2; mel = 1,3,5-C3N3(NH2)3). Each structure displays numerous hydrogen bond interactions between bisphosphonate anions, the (alkyl)ammonium cations and water molecules resulting in 3-D network materials. Compounds 1, 7 and 8 display identical 2-D sheets composed of [LH3]2− anions and water molecules approximately 12 Å thick and pillared by the [enH2]2+ or [onH2]2+ cations or a double layer of [PheaH]+ cations. A similar pillared structure is also observed in compound 9 where the 2-D anion layers are separated by regions of hydrogen bonded and π-stacked [melH]+ cations. The anion layer, although similar to that of compounds 1, 7 or 8, contains a significantly higher proportion of water molecules. The substituted ethylene diamine derivatives 2, 3, and 4 also display a consistent (but not identical) set of flat 2-D sheets of [LH3]2− anions and water molecules, with the organic diammonium cations and further water molecules sandwiched in between. In contrast to the above lamella type structures, the cda and xda derivatives, 5 and 6, comprise tessellated columns of anion and cations. A consistent feature of all the above structures is the head-to-tail arrangement of [LH3]2− anions held by strong, charge assisted, N(H)⋯O hydrogen bonds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...