Synthesis and investigations of In2S3:Ho3+ quantum dots on doping induced changes†
Abstract
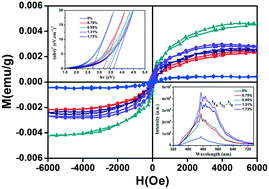
Diluted magnetic semiconductor (DMS) quantum dots have been investigated extensively because of their potential applications in spintronic devices that combine the charge and spin properties of electrons in a material. Herein, the In2S3:Ho3+ quantum dots (3–5 nm) with different doping concentrations have been synthesized using the facility built by us and the corresponding growth mechanism is proposed and discussed in detail. We investigated the effect of different Ho3+ content on the optical and magnetic properties. The absorption and emission spectra exhibit a strong quantum size confinement effect and a large Stokes shift. The band gap energy can be tuned by doping concentration varying from 3.19 to 3.62 eV. The emission processes are assigned to the excitonic recombination and near-doping/near-defect excitonic luminescence, respectively. Excess Ho3+ content reduces the intensity of photoluminescence as a result of concentration quenching. Room temperature ferromagnetism is observed from VSM measurement. The change of saturation magnetizations with various Ho3+ doping concentrations is explained and discussed based on BMP theory. In addition, the band gap distribution and the chemical bonding mechanism are clearly illustrated using VASP first-principles calculations. This study provides experimental and theoretical guidance for designing and synthesizing unique spintronic materials, which can promote the development of spintronic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...