Na–CO batteries: devices to trap CO†
Abstract
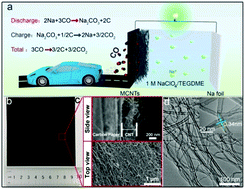
Metal–gas batteries that remove CO gases would provide enormous environmental benefits. We report here Na–CO batteries using the combination of a sodium anode and a binder-free multiwall carbon nanotube cathode with a CO reactant. The constructed Na–CO batteries show a high discharge capacity of 8000 mA h g−1 based on the mass of carbon nanotubes (corresponding to ∼865.9 W h kg−1 based on the mass of total active materials) and a stable cycling of 70 cycles with an increased gap of only 3.7 mV. This work offers a promising strategy for efficient utilization of CO to generate electricity through an electrochemical conversion method.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...