Quantitative chemoproteomic profiling reveals multiple target interactions of spongiolactone derivatives in leukemia cells†
Abstract
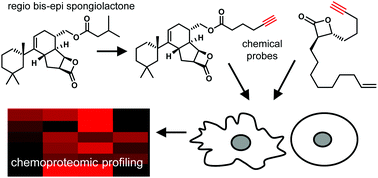
The spongiolactones are marine natural products with an unusual rearranged spongiane skeleton and a fused β-lactone ring. These compounds have potential anticancer properties but their mode of action has yet to be explored. Here we employ activity-based protein profiling to identify the targets of a more potent spongiolactone derivative in live cancer cells, and compare these to the targets of a simpler β-lactone. These hits provide the first insights into the covalent mechanism of action of this natural product class.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...