Nucleobase-modified polyamidoamine-mediated miR-23b delivery to inhibit the proliferation and migration of lung cancer†
Abstract
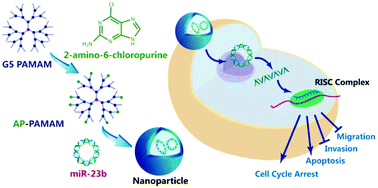
The nucleobase analogue 2-amino-6-chloropurine was modified on the surface of polyamidoamine (PAMAM) to construct a derivative AP-PAMAM, and then it was used as a gene carrier for miR-23b delivery to achieve the anti-tumor effects. The carrier AP-PAMAM could condense miR-23b into stable nanoparticles with a particle size of 97.3 nm (N/P ratio of 50), which was favorable for the cellular uptake of nanoparticles. Compared with PAMAM, AP-PAMAM exhibited an obviously enhanced transfection efficiency through the transfection assay of plasmids pEGFP-N3 and pGL-3. Using the human lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549 as a model, AP-PAMAM-mediated miR-23b delivery could achieve a stronger anti-proliferative effect than PAMAM/miR-23b. The inhibition of cell proliferation was elucidated to be associated with the apoptotic induction (apoptotic ratio of 23.2%) and S phase arrest owing to the decreased expression level of cyclin D1. Meanwhile, the AP-PAMAM-mediated miR-23b delivery could suppress the cell migration and invasion of cancer cells through wound healing and Transwell migration assays. In summary, the PAMAM derivative-mediated miR-23b delivery could be a promising strategy for achieving tumor gene therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...