Surface coupling strength of gold nanoparticles affects cytotoxicity towards neurons†
Abstract
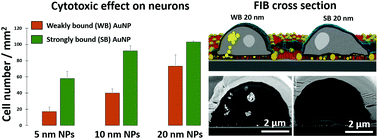
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are versatile nanomaterials which are frequently used to manipulate and study cellular behavior on the nanometer scale. However, it has been recognized that freely diffusing colloidal particles can possess severe cytotoxicity. One strategy to overcome this harmful side effect is to tether the nanoparticles to sample surfaces. In this study, the cytotoxicity of immobilized AuNPs is investigated as a function of their sizes, surface density, and binding strength. The AuNPs are modified with positively charged aminoalkyl thiol molecules to promote the cell adhesion, while their background is passivated. Primary cortical neurons are cultured on the particle modified samples and the survival of the cells is investigated. This study reveals that besides the particle size, the particle binding strength influences the cytotoxicity during long time culture. Weakly bound particles dramatically decrease the survival of neurons while strongly bound particles hardly harm the neurons. More importantly, it is found that weakly bound AuNPs can cause higher cytotoxic effects on cells than colloidal particles dispersed in the culture medium. These results propose that the toxic effect of surface bound particles can be severe and therefore requires consideration, if nanoparticle modified surfaces are used for cell experiments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...