A rapid albumin-binding 5-fluorouracil prodrug with a prolonged circulation time and enhanced antitumor activity
Abstract
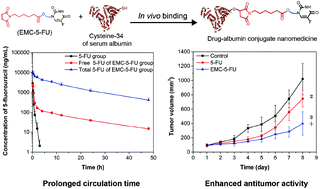
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is an antimetabolite widely used in the treatment of a variety of solid tumors. However, its clinical applications are greatly hindered by a very short residence time in blood circulation and non-specific distribution in the body. In order to overcome these challenges, 1-alkylcarbonyloxymethyl 5-FU was designed and linked with a maleimide group to form an albumin-binding 5-FU prodrug, named EMC-5-FU. In vitro incubation with bovine serum albumin (BSA) and fresh rat blood proved that the prodrug bound rapidly to cysteine-34 to form the drug–albumin conjugate nanomedicine. The conjugate BSA–EMC-5-FU was stable under acidic and neutral conditions but an unstable compound to release 5-FU in alkaline solution, and such a property was used for the determination of total 5-FU concentration in plasma. The t1/2 and AUC values of total 5-FU after an intravenous injection of EMC-5-FU to SD rats were significantly increased, about 43-fold and 93-fold higher than those of 5-FU following 5-FU intravenous administration, respectively. In vivo fluorescence images of EMC-Cy5 indirectly demonstrated the selective tumor accumulation of EMC-5-FU. In H22 tumor-bearing mice models, treatment with EMC-5-FU was more efficacious in tumor inhibition compared to 5-FU intravenous administration. In conclusion, a rapid albumin-binding prodrug strategy addresses concerns related to the poor circulation half-life and non-specific distribution of anticancer drugs, and paves the way for the development of in vivo-forming nanomedicines in clinical cancer therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...