Recyclable trypsin immobilized magnetic nanoparticles based on hydrophilic polyethylenimine modification and their proteolytic characteristics†
Abstract
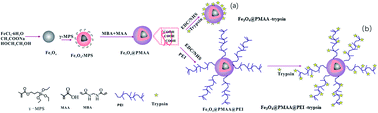
In this work, recyclable trypsin immobilized magnetic nanoparticles based on hydrophilic branched polyethylenimine (PEI) modification were synthesized under mild conditions. The amount of the immobilized enzyme was increased greatly by introducing branched PEI onto poly(methacrylic acid) (PMAA) modified Fe3O4 microspheres (denoted as Fe3O4@PMAA@PEI). Trypsin, a model enzyme for this study, was immobilized by Cu2+ with metal chelation to Fe3O4@PMAA@PEI. Compared with Fe3O4@PMAA nanoparticles, the abundant amino groups of the PEI layer not only increased the amount of the immobilized enzyme, but also improved the hydrophilicity of the material to avoid nonspecific protein adsorption. The performance of this material was evaluated by digesting bovine serum albumin (BSA), myoglobin and cytochrome C, followed by MALDI-TOF-MS analysis. Compared with in-solution digestion, not only the sequence coverage was improved (70.0 ± 3.1% vs. 40.0 ± 2.3% for BSA, 92.0 ± 2.4% vs. 81.0 ± 0.8% for myoglobin and 90.0 ± 3.0% vs. 56.0 ± 1.8% for cytochrome C), but also the digestion time was decreased from 24 h to 10 min. Furthermore, the relative standard deviation values (RSDs) of the sequence coverage of BSA were 3.0% for five consecutive digestions and 2.2% for particles from different batches (n = 3), showing good reproducibility. The Fe3O4@PMAA@PEI-trypsin can endure at least 7 times usage and still maintain good digestion performance after being stored at 4 °C for 25 days. When applied to complex samples, more proteins were identified from the extract of a rat liver than in-solution based digestion (582 vs. 496), with a shorter reaction time of 10 min.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...