MoS2-based sensor for the detection of miRNA in serum samples related to breast cancer†
Abstract
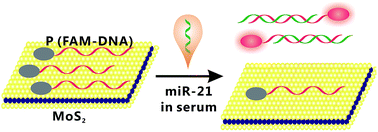
Early diagnosis of cancer is critical for the treatment of patients, and can reduce the risk of death. Breast cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors in women, and miR-21, as an important breast cancer biomarker, can be helpful for the early diagnosis of breast cancer. In this work, we have developed an efficient, sensitive and specific fluorescence sensor based on the novel nanomaterial molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) to detect miR-21. The novel nanomaterial MoS2 was introduced to a fluorescent dye-labeled DNA probe to fabricate the fluorescence sensor, and then non-complementary miRNA, one-base mismatched miRNA and complementary miR-21 were separately introduced to the sensor to hybridize with the DNA probe. By monitoring the change of the fluorescence signal before and after DNA-miRNA hybridization, miR-21 could be detected. We found that the sensor could discriminate complementary miR-21 from one-base mismatched miRNA and non-complementary miRNA successfully. Furthermore, the biosensor was able to detect miR-21 down to a concentration of 500 pM, and the detection could be completed in only 40 min. The novel MoS2 fluorescence sensor, with the advantages of fast analysis, high sensitivity and specificity, and low cost, is suitable for miR-21 detection which is of great importance for the early diagnosis of breast cancer. What’s more, the novel sensor, with high sensitivity and selectivity, was also used to detect miR-21 in serum samples, making it a promising method for detection in real samples from patients with cancer. Thus the novel MoS2 fluorescence sensor shows huge potential for early diagnosis of cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...