CNT-anchored cellulose fluorescent nanofiber membranes as a fluorescence sensor for Cu2+ and Cr3+†
Abstract
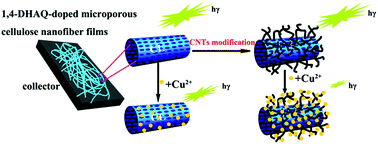
1,4-Dihydroxyanthraquinone (1,4-DHAQ, a fluorophore) doped carbon nanotubes@cellulose (1,4-DHAQ-doped CNTs@CL) nanofibrous membranes have been prepared via electrospinning and subsequent deacetylation in this work. They have been successfully applied for highly sensitive detection of Cu2+ in aqueous solution. The surface area per unit mass (S/M) ratio of the nanofibrous membranes was enhanced by incorporating the CNTs into cellulose. Moreover, the excellent metal ion sorption capability of the CNTs improved the sensitivity of the sensing materials. Both of the two points mentioned above significantly improved the lower detection limit of fluorescence sensing as expected. As the resultant byproduct of Cu2+-contaminated 1,4-DHAQ-doped CNTs@CL nanofibrous membranes showed recovered fluorescence by extra addition of Cr3+ in solution, 1,4-DHAQ and Cu2+ co-doped CNTs@CL (denoted as 1,4-DHAQ/Cu2+ co-doped CNTs@CL) microporous nanofibrous membranes were further fabricated for the fluorescence enhancement detection of Cr3+ in aqueous solution. It was found that the fluorescence intensity of the 1,4-DHAQ-doped CNTs@CL nanofibrous membranes linearly decreased with Cu2+ concentration in the range of 0–2.2 × 10−8 M, while that of the 1,4-DHAQ/Cu2+ co-doped CNTs@CL nanofibrous membranes linearly increased with Cr3+ concentration in the range of 0–2.4 × 10−8 M. The excellent fluorescence sensing properties of the 1,4-DHAQ-doped CNTs@CL and 1,4-DHAQ/Cu2+ co-doped CNTs@CL nanofibrous membranes for Cu2+ and Cr3+ were further demonstrated by using polluted lake waters, proving their potential applications in environmental monitoring areas. The design concept mentioned in this work might also open a door to the design of other effective fluorescence probes with high sensitivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...