In situ cocoa beans quality grading by near-infrared-chemodyes systems†
Abstract
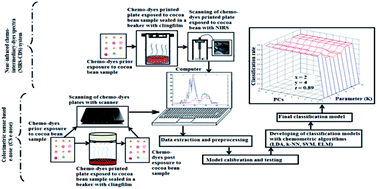
Fermentation level is a key bean quality indicator in the cocoa industry. A colorimetric sensor e-nose (CS e-nose) and an innovatively designed near infrared chemo-intermediary-dyes spectra technique (NIR-CDS) combined with four chemometric algorithms – extreme machine learning (ELM), support vector machine (SVM), linear discriminant analysis (LDA) and k-nearest neighbors (k-NN) – were applied to classify 90 sampled cocoa beans into three quality grades – fully fermented, partially fermented and non-fermented. The CS e-nose (89% ≤ Rp ≤ 94%) and NIR-CDS (85% ≤ Rp ≤ 94%) achieved comparable classification rates, with the systems' data cluster analysis yielding cophenetic correlation coefficients of 0.85–0.89. Both systems combined with SVM and ELM achieved a high classification rate (Rp = 94%) and could be applied to cocoa bean quality classification on an in situ and nondestructive basis. This novel NIR-CDS technique proved a pragmatic approach for the selection of sensitive chemo-dyes used in the fabrication of e-nose colorimetric sensor arrays compared with the hitherto trial-and-error method, which is time-consuming and dye-wasteful. The technique could also be deployed in near-infrared systems for the detection of volatile (gaseous) compounds, which previously had been a limitation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...