Development and validation of a novel fluorometric sensor for hydrogen peroxide monitoring in exhaled breath condensate†
Abstract
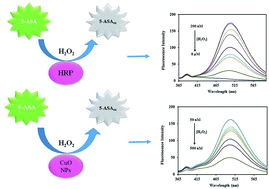
A novel fluorometric sensor based on catalyzed 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA)/H2O2 systems was developed to detect trace levels of H2O2 in exhaled breath condensate (EBC). It relies on the oxidative conversion of the fluorophore (5-ASA) into its non-fluorescent product (5-ASAox). The fluorescence intensity of 5-ASA was lost by the reaction with H2O2 in the presence of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or CuO nano-particles (NPs). As the decrease in the fluorescence intensity is proportional to H2O2 concentration, new methods were developed for the monitoring of H2O2 in EBC samples using the HRP- and CuO NP-catalyzed 5-ASA/H2O2 assays. The methods were optimized and validated according to the standard validation techniques in EBC samples. Under the optimized experimental conditions, linear calibration graphs were obtained in the range of 200–8000 nmol L−1 and 50–500 nmol L−1 for the HRP-catalyzed and CuO NP-catalyzed 5-ASA/H2O2 assays, respectively. The limits of detection, evaluated as 3Sb/m (where Sb and m are the standard deviation of the blank and slope of the calibration curves, respectively), were found to be 137.0 nmol L−1 and 33.6 nmol L−1 for HRP-catalyzed and CuO NP-catalyzed 5-ASA/H2O2 systems, respectively. These developed systems are promising for application in the detection of trace amounts of H2O2 in oxidative stress studies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...