A label-free fluorescence nanosensor for the determination of adrenaline based on graphene quantum dots†
Abstract
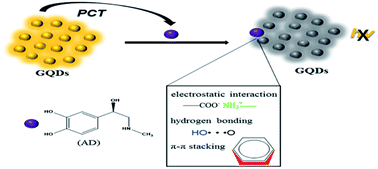
In this paper, graphene quantum dots (GQDs) were employed to design an effective and simple fluorescence biosensor for the detection of adrenaline (AD). AD could quench the fluorescence of GQDs on account of photoinduced charge transfer (PCT) by the noncovalent interaction with GQDs. Hence, the concentration of AD could be effectively monitored according to the variation of the fluorescence signal of GQDs. Under the optimized conditions, the fluorescence intensity ratio I0/I versus the concentration of AD (1–200 μM) displayed brilliant linearity. The developed method was also applied to the investigation of AD concentration in real human serum samples and yielded satisfactory results.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...