A strategy for rapid identification of healthy Tegillarca granosa from among those contaminated with unspecified heavy metals using infrared spectroscopy
Abstract
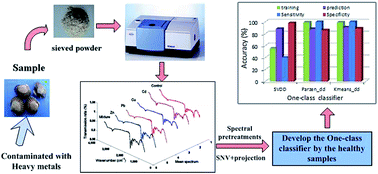
A novel strategy for rapidly distinguishing healthy Tegillarca granosa samples from among those subjected to unspecified heavy metal contamination is here introduced using an infrared spectroscopy approach. Heavy metal contamination in ocean environments is complex, and using the common traditional multi-class classification model for heavy metal analysis is fraught with uncertainty due to the limited reference information available for classifier training. Therefore, the combination of the traditional classification model and infrared spectroscopy is incapable of identifying healthy Tegillarca granosa from among those contaminated with unspecified heavy metals. Identification of healthy Tegillarca granosa is considered as a one-class problem, and the spectral data of healthy Tegillarca granosa were considered as a specific type of information used for training. The data description boundary was determined; a one-classifier assigns a test sample to that class according to whether it falls within (healthy samples) or outside (heavy metal contaminated samples) the boundary. In order to reduce the spectral dimension, component factors were extracted to eliminate redundant spectral variables from projection processing. The performance of different preprocessing methods, including standard normal variate, first derivative, second derivative, and standard normal variate-first derivative, was compared. Three one-class models using whole spectra and component factors were developed, including the support vector data description classifier, Parzen data description classifier, and K-means data description classifier. The K-means data description classifier combined with standard normal variate, standard normal variate-first derivative preprocessed spectra and component factors showed optimal prediction results, and a sensitivity of 100%, a specificity of 91.60% and a prediction accuracy of 99.17% were achieved. Furthermore, the proposed strategy can allow healthy samples to be distinguished from those with unspecified contamination such as organic substance contamination.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...