A glucometer-based strategy for sensitive DNA methyltransferase activity detection via a polymerization nicking reaction and enzyme amplification†
Abstract
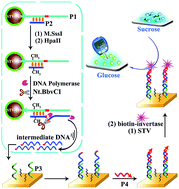
DNA methyltransferase (MTase) is closely related to the DNA methylation level in many biological processes and has been recognized as a predictive cancer biomarker which occurs before other signs of malignancy and a therapeutic target in cancer treatment. Thus, it is significant to develop a simple and sensitive method to detect DNA MTase activity. Here, a dual amplification strategy for simple and sensitive detection of DNA MTase activity based on a polymerization nicking reaction (PNR) and invertase enzyme amplification by using a glucometer as a signal transducer is proposed. A trifunctional dsDNA probe is designed including a methylation site for MTase, a complementary domain of the recognition sequences for the nicking enzyme and an amplification domain as the template to produce intermediate DNA sequences. The presence of a DNA MTase target causes dsDNA methylation and thus enables the cyclic PNR to generate numerous intermediate DNA sequences which act as bridges to bind with P3 and P4, resulting in the successful involvement of invertase signal molecules. The invertase enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose to generate glucose, monitored by using a glucometer whose readings are utilized for quantification. Attributing to the high efficiency of the PNR and invertase enzyme catalysis reaction, a trace amount of targets causes the generation of massive intermediate DNA sequences and abundant glucose to amplify the signal response of the glucometer for quantitative analysis. This strategy is not only sensitive toward the DNA MTase activity with a detection limit of 0.1 U mL−1, but also selective against other two cytosine MTases (HaeIII MTase and AluI MTase). Besides, two anticancer drugs (5-azacytidine and 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine) are used as model inhibitors to test the inhibitor screening ability and the outcome is satisfactory. These results indicate that our method holds great promising applications in early cancer diagnosis and therapeutics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...