A sample pretreatment method to suit the metabolomic analysis of Bacillus licheniformis based on GC-MS
Abstract
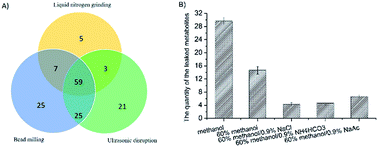
Selection of an appropriate sample pretreatment method is crucial to the quality of metabolomic analysis. Great variability exists in terms of sample pretreatment techniques for microbial metabolomics in the current literature, and it is unknown that a suitable sample preparation procedure for metabolomic analysis of Bacillus licheniformis. To improve the quality of metabolomic analysis of B. licheniformis based on GC-MS, the leakage of intracellular metabolites with five different quenching solvents was compared in this study, and 60% methanol/0.9% NH4HCO3 and 60% methanol/0.9% NaCl were found to have the least leakage; effects of different cell disruption methods including bead-milling, liquid nitrogen grounding and ultrasonication on the extraction of metabolites were compared. The bead-milling method was shown to have the best extraction efficiency. The effects of derivatization time (0.5–2.5 h) on the relative abundance of metabolite distribution were also compared and derivatization for 2 h was shown to be adequate. The optimal sample pretreatment method for metabolomic analysis of B. licheniformis was determined as follows: 60% methanol/0.9% NH4HCO3 as a quencher, bead-milling for cell disruption and a derivatization time of 2 h. With this method, 127 metabolites were detected, including a large number of amino acids, organic acids and carbohydrates in B. licheniformis. This study will facilitate the comprehensive metabolic analysis of this important industrial microbe.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...