Chemical modification of antibodies enables the formation of stable antibody–gold nanoparticle conjugates for biosensing†
Abstract
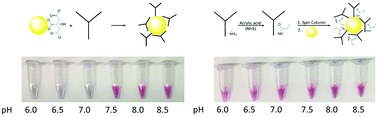
Antibody-modified gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are central to many novel and emerging biosensing technologies due to the specificity provided by antibody–antigen interactions and the unique properties of nanoparticles. These AuNP-enabled assays have the potential to provide significant improvements in sensitivity and multiplexed analysis compared to conventional immunoassays. However, a major challenge for these AuNP platform technologies is the synthesis of stable antibody–AuNP conjugates that resist aggregation in high salt environments and biological matrices. Moreover, synthetic strategies to form stable conjugates often require different solution conditions, e.g., pH, for each unique antibody. Herein we describe our effort to develop an approach to chemically modify lysine residues on antibodies to facilitate the formation of stable antibody–AuNP conjugates over a wide pH range. In this work, we systematically investigated the immobilization of native and chemically modified antibodies to 60 nm citrate-capped AuNPs as a function of pH and evaluated the stability of the antibody–AuNP conjugate in a saline environment. We have developed a method to chemically modify the lysine residues on an antibody prior to conjugation to the AuNP that results in stable conjugates over a wide pH range (6.0–8.5). Amino acid analysis and zeta potential measurements of native and modified antibodies reveal that the requisite modification correlates with the number of lysine residues, and a reduction in positive charge contribution from protonated lysine is required to form stable, pH-independent conjugates. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the chemically modified antibodies maintain antigen-binding capabilities. We apply this novel conjugation strategy to develop a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)-based assay for the accurate subtyping of avian influenza viruses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...