A universal and enzyme-free immunoassay platform for biomarker detection based on gold nanoparticle enumeration with a dark-field microscope†
Abstract
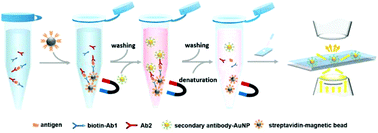
Developing an enzyme-free, non-amplification strategy for biomarker detection with universality and easy implementation is of central importance in clinical diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. Herein, we report for the first time a universal and enzyme-free magnetic bead-based sandwich-format immunoassay platform for biomarker detection by combining secondary antibody functionalized AuNPs and automatic AuNP counting readout. For the prostate specific antigen (PSA), the detection limit is found to be 1 ng mL−1, and the spike recoveries (n = 3) with 10% fetal bovine serum are 113.5% for 2 ng mL−1 and 107.7% for 10 ng mL−1. The assay also presents reasonable repeatability as indicated by the coefficient of variance of 13.1% with 5 measurements in 60 days. This strategy has been successfully applied to the determination of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), demonstrating the universality of this strategy. Our proposed non-amplification platform presents sensitivity comparable to that of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with better repeatability; and more importantly, our method has better simplicity than most of the amplification-based methods, and thus is more suitable for routine analysis. The highlights of our work suggest that it is a promising method and would be potentially an alternative for ELISA in laboratories where routine analyses are intensively performed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...