Electrochemical behaviour at a liquid-organogel microinterface array of fucoidan extracted from algae†
Abstract
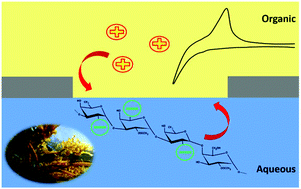
Fucoidans are sulfated polysaccharides mostly derived from algae and used in a number of applications (e.g. nutrition, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and biomaterials). In this study, the electrochemical behaviour of fucoidans extracted from two algal species (Undaria pinnatifida and Fucus vesiculosus) was assessed using voltammetry at an array of micro-interfaces formed between two immiscible electrolyte solutions (μITIES) in which the organic electrolyte phase was gelled. Cyclic voltammetry revealed an adsorption process when scanning to negative potentials, followed by a desorption peak at ca. −0.50 V on the reverse scan, indicating the electroactivity of both fucoidans. U. pinnatifida fucoidan showed a more intense voltammetric signal compared to F. vesiculosus fucoidan. In addition, use of tridodecylmethylammonium (TDMA+) or tetradodecylammonium (TDDA+) as the organic phase electrolyte cation provided improved detection of both fucoidans relative to the use of bis(triphenylphosphoranylidene)ammonium (BTPPA+) cation. Application of adsorptive stripping voltammetry provided a linear response of current with fucoidan concentration in the range 2–20 μg mL−1 for U. pinnatifida fucoidan (with TDMA+) and 10–100 μg mL−1 for F. vesiculosus fucoidan (with TDDA+). The combination of TDMA+ in the organic phase and adsorptive pre-concentration for 180 s afforded a detection limit of 1.8 μg mL−1 fucoidan (U. pinnatifida) in aqueous phase of 10 mM NaOH and 2.3 μg mL−1 in synthetic urine (pH adjusted). These investigations demonstrate the electroactivity of fucoidans at the μITIES array and provide scope for their detection at low μg mL−1 concentrations using this approach.
- This article is part of the themed collection: In memory of Craig Lunte


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...