An arylboronate locked fluorescent probe for hypochlorite†
Abstract
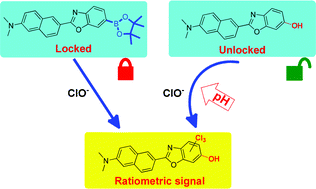
An unusual arylboronate based fluorescent probe R1 was synthesized for the selective and sensitive detection of ClO−. A detailed mechanistic study revealed that R1 reacted with ClO− through an oxidation to chlorination mechanism, and the arylboronate moiety in R1 acted as a “lock” to eliminate the effects of pH fluctuations. With this design strategy, R1 was successfully used to detect as low as 6.4 nM of ClO− over other ROS species in a wide pH range from 4.5 to 9.0.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...