An efficient two-photon fluorescent probe for measuring γ-glutamyltranspeptidase activity during the oxidative stress process in tumor cells and tissues†
Abstract
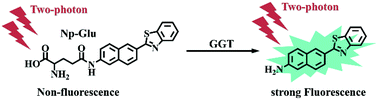
Oxidative stress, a disturbance in the balance between oxidant/antioxidant ratios, is associated with cancer, aging, inflammation, neurodegenerative diseases and other conditions. γ-Glutamyltranspeptidase (GGT) is a redox-related enzyme that plays a key role in mitigating the effects of oxidative stress by maintaining cellular glutathione (GSH) metabolism and homeostasis. Therefore, oxidative stress will upregulate the intracellular GGT level. To better understand the major pathophysiological resist mechanism to oxidative injury in mediating many disease states, we designed and synthesized a novel two-photon (TP) fluorescent turn-on probe, Np-Glu, for GGT detection and bioimaging. Under the optimized conditions, Np-Glu exhibited remarkable fluorescence enhancement (150-fold), good selectivity and high sensitivity (LOD is 0.033 U L−1), with a wide linear concentration range (0–50 U L−1). More importantly, the probe Np-Glu was successfully applied in one-photon and TP fluorescence imaging of GGT activity in an oxidative stress model in living cells and tissues, suggesting Np-Glu as an ideal indicator for clinical and biological samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...