Quantitative NMR of quadrupolar nucleus as a novel analytical method: hydrolysis behaviour analysis of aluminum ion†
Abstract
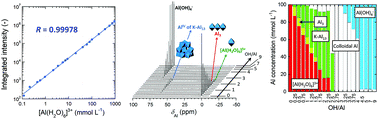
In this study, quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance (qNMR) spectroscopy of quadrupolar nuclei has been established. The complicated hydrolysis behavior of the Al3+ ion, which causes fish poisoning and inhibits the growth of plants in environmental water, was clarified by 27Al qNMR spectroscopy. Highly accurate simultaneous multicomponent quantitative analysis of various hydrolyzed forms of the Al ion was achieved in a non-destructive manner. The calibration curve of the external standard aqueous Al(NO3)3 solution showed excellent linearity over a very wide concentration range from 1 × 10−4 to 1 mol L−1 (an increase in concentration of 10 000 times), with a simple experimental and analytical procedure. Furthermore, the weaknesses of the conventional Ferron assay and the advantages of 27Al qNMR spectroscopy were considered. The quantitative determination error for the free [Al(H2O)6]3+ ion and the trinuclear complex, which has a high complexation rate, is higher in the Ferron assay than in the 27Al qNMR technique. The concentrations of four Al species were directly determined by 27Al qNMR, namely, free [Al(H2O)6]3+, the trinuclear complex, Al(OH)4−, and tridecameric hydrolyzed Al, which has a Keggin structure. The concentration of the tridecamer rapidly increased until 100 min after NaOH addition, and showed a local maximum after 1 week. In addition, the concentration of colloidal Al hydroxide, which cannot be detected by NMR spectroscopy, was determined by numerical analysis. This species was generated in the initial stage of reaction, and then the tridecamer formed very slowly.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...