Combined use of AFM and soft X-ray microscopy to reveal fibres’ internalization in mesothelial cells
Abstract
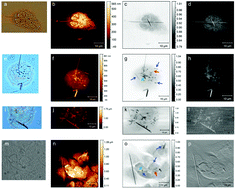
Nanotoxicology and nanomedicine investigations often require the probing of nano-objects such as fibres and particles in biological samples and cells, whilst internalization and intracellular destiny are the main issues for in vitro cellular studies. Various high resolution microscopy techniques are well suited for providing this highly sought-after information. However, sample preparation, nanomaterial composition and sectioning challenges make it often difficult to establish whether the fibres or particles have been internalized or they are simply overlaying or underlying the biological matter. In this paper we suggest a novel suitable combination of two different microscopic techniques to reveal in intact cells the uptake of asbestos fibres by mesothelial cells. After exposure to asbestos fibres and fixation, cells were first analysed under the AFM instrument and then imaged under the TwinMic soft X-ray microscope at Elettra Sincrotrone. The suggested approach combines standard soft X-ray microscopy imaging and AFM microscopy, with a common non-invasive sample preparation protocol which drastically reduces the experimental uncertainty and provides a quick and definitive answer to the nanoparticle cellular and tissue uptake.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...