Superwetting comonomers reduce adhesion of E. coli BL21†
Abstract
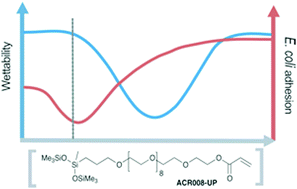
The adhesion of Escherichia coli to copolymers of methacrylates and a trisiloxane-polyether acrylate surfactant was found to be at a minimum with copolymers containing a low (20%) fraction of the surfactant monomer. Rather than wettability, hardness, or water uptake, adhesion was found to be limited by the presence of low concentrations of bound surfactant that can interact with hydrophobic domains on the bacterium inhibiting anchoring to the polymer surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...