Morphology-controlled self-assembly of a ferrocene–porphyrin based NO2 gas sensor: tuning the semiconducting nature via solvent–solute interaction†
Abstract
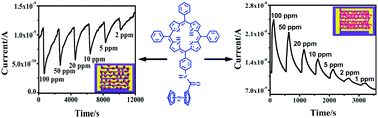
A novel unsymmetrical ferrocene–porphyrin derivative, namely 5-(4-ferrocamidophenyl)-10,15,20-triphenylporphyrin (H2FcPor), is designed, synthesized and characterized. The self-assembly properties of this novel ferrocene–porphyrin in methanol and n-hexane are comparatively investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), the X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique, Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy and electronic absorption spectroscopy. Intermolecular π–π interaction in cooperation with the solvent–solute interaction and the absence or presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding leads to the formation of nanospheres and nanobelts in methanol and n-hexane, respectively. When applied as gas sensors, both the nanospheres and the nanobelts exhibit excellent gas sensitivity, and good stability and selectivity at room temperature for NO2 detection. Under the same measurement conditions, the detection limit and recovery times of nanobelt gas sensors are lower and faster than those for nanosphere gas sensors. Surprisingly, the nanospheres exhibit a normal n-type gas-sensing response to NO2, while the nanobelts display p-type gas-sensing behaviour in different NO2 concentration ranges. The abnormal sensing behavior with transition from n- to p-type NO2 sensing is tuned by solvent–porphyrin molecule interaction and molecular packing mode for the first time.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...