Stretchable magneto-dielectric composites based on raspberry-shaped iron oxide nanostructures
Abstract
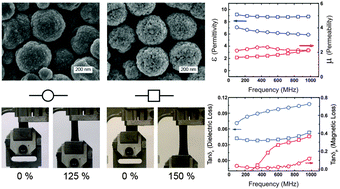
Stretchable magneto-dielectric composites were prepared using collectively assembled iron oxide nanostructures as fillers in an elastomer (polydimethylsiloxane) matrix. These raspberry-shaped nanostructures (RSNs), synthesized by a one-pot polyol solvothermal method, consist of oriented aggregates of iron oxide nanocrystals. The oriented aggregation of nanocrystals generates a large interface between nanograins significantly reducing their surface oxidation, improving crystal quality and preventing the formation of surface and volume spin canting. Therefore these iron oxide RSNs display low coercivity with enhanced saturation magnetization (MS). The use of such citrated RSN as filler material with improved magnetization and low coercivity allowed the fabrication of magneto-dielectric composites that can attain permeability values reaching 2.3 with magnetic loss values limited to 0.11. The resulting composites can also be stretched up to 155% strain before failure due to good adhesion between the elastomer and citrate capped RSNs. In addition, the composition of these fillers was altered to adjust the resonance frequency of the resulting composite material. Stretchable magneto-dielectric composites consisting of maghemite-rich RSNs and magnetite-rich RSNs demonstrated resonance frequencies similar to the spherical ferromagnetic resonance of maghemite and magnetite, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...