Templated solvothermal synthesis of magnesium silicate hollow nanospheres with ultrahigh specific surface area and their application in high-performance protein adsorption and drug delivery†
Abstract
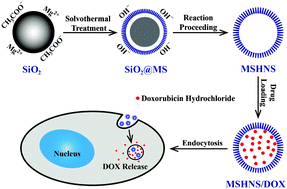
Magnesium silicate nanostructured biomaterials with good biocompatibility and high adsorption capacity for drugs and proteins are promising for applications in various biomedical fields. However, the applications of magnesium silicate nanostructured biomaterials in anticancer drug delivery and protein adsorption have rarely been reported so far. Herein, we report a facile strategy for the synthesis of magnesium silicate hollow nanospheres (MSHNSs) by a classical Stöber method and a template based solvothermal process. The as-prepared MSHNSs have an ultrahigh specific surface area of 585.6 m2 g−1, ultrahigh hemoglobin (Hb) protein adsorption capacity (1262 mg g−1) and high doxorubicin (DOX) drug loading capacity (559 mg g−1). Moreover, the as-prepared MSHNS/DOX drug delivery system exhibits sustained and pH-responsive drug release performance. Compared with free DOX, the MSHNS/DOX drug delivery system exhibits higher anticancer activity in vitro, and thus it is promising for applications in anticancer treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...