The immobilization of a direct thrombin inhibitor to a polyurethane as a nonthrombogenic surface coating for extracorporeal circulation
Abstract
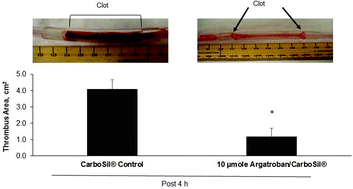
A biomaterial with both antithrombin and antiplatelet properties is the ideal surface for use in extracorporeal circulation (ECC) as it targets both fibrin generation and platelet adhesion. A hemocompatible surface coating avoids the need for systemic anticoagulation by providing a local anticoagulant effect at the polymer–blood interface. Previous work has demonstrated the potential use of argatroban, a direct thrombin inhibitor, as a nonthrombogenic material for extracorporeal devices. The work reported here focuses on the characterization of argatroban linked to a polyurethane–silicone polymer, CarboSil®. Chemical immobilization, the amount of argatroban, incubation times, and saturation point were evaluated to achieve maximal antithrombin activity at the polymer surface. Cross-linked polymer coatings reacted with 10 and 30 μmole of argatroban were prepared and tested. These coatings resulted in argatroban activity levels of 0.131 μM and 0.446 μM, respectively. After refining the cross-linking process, argatroban activity increased by approximately 3.6 fold. Maintenance of activity and leaching from the polymer surface were also evaluated. Using the refined process for linking argatroban to polymer, the resulting polymer was applied as a surface coating to the inner lumen of poly(vinyl chloride) ECC circuit tubing and its antithrombin effect evaluated using a 4 h rabbit ECC model. Following 4 h of blood exposure, the argatroban circuit demonstrated significantly less thrombus formation compared to the control CarboSil® coating with a 4.1 cm2 thrombus average area for the control coating compared to 1.2 cm2 for the argatroban coating (n = 4). There was no significant change in thrombin time from baseline in plasma from animals in which the argatroban coated circuit was used, with a thrombin time of 16.2 s at t = 0 and 14.5 s after 4 h. These results demonstrate the potential efficacy of immobilized argatroban as a hemocompatible biomaterial for extracorporeal life support devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...