Multiple effects of Bi doping in enhancing the thermoelectric properties of SnTe†
Abstract
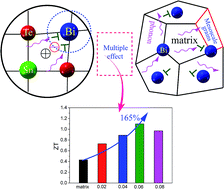
We studied the effect of doping with Bi on the thermoelectric properties of SnTe-based materials. Doping with Bi reduced the density of holes and increased the Seebeck coefficient over a wide temperature range as a result of modulation of the carrier concentration and an increase in the density of states effective mass. The lattice thermal conductivity was also greatly reduced as a result of the wide frequency range of phonon scattering by multiscale architectures derived from Bi doping. A maximum ZT value of c. 1.1 at 873 K was obtained in Sn0.94Bi0.06Te, an enhancement of 165% compared with the undoped sample.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...