Photochemical reduction of carbon dioxide coupled with water oxidation using various soft-oxometalate (SOM) based catalytic systems†
Abstract
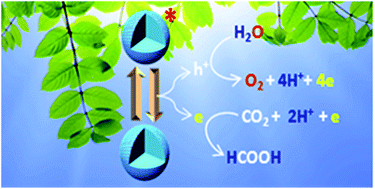
Simultaneous CO2 reduction and water oxidation as a coupled process is an important challenge in the quest of clean energy production. Herein, we report a metal oxide based heterogeneous catalytic system, which not only couples CO2 reduction with water oxidation, but also provides very high turnover number for CO2 reduction with scalability. Such a catalytic system can simultaneously oxidize water and release the generated electrons for reduction of CO2 with a maximum turnover number and turnover frequency as high as 1.4 × 106 and 610 s−1, respectively, following effective catalyst concentration; whereas, turnover number and turnover frequency is 1366 and 1380 h−1 per mole of catalyst, respectively. The starting materials for this catalytic process are CO2 and water while the end products are oxygen and formic acid and in few cases, formaldehyde. The prospect of using the formic acid generated during our process in fuel cells to generate green energy is also worth mentioning.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...