N-, P- and Fe-tridoped nanoporous carbon derived from plant biomass: an excellent oxygen reduction electrocatalyst for zinc–air batteries†
Abstract
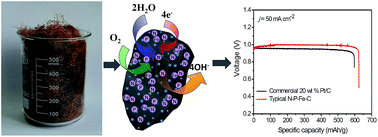
The zinc–air battery is a promising energy device because of its high energy density and high safety. Developing efficient electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in air electrode is of great importance for high-performance zinc–air batteries. Herein, we first report N, P and Fe-tridoped nanoporous carbon ORR electrocatalysts derived from plant biomass corn silk. It is a cheap, accessible and recyclable biomass, which can offer a good basis for developing catalysts with low-cost and high yield production. The electrocatalysts were prepared by a hydrothermal process and a two step heat treatment process. The Fe element doped in the catalyst mainly came from FeCl3 and the P element came from corn silks. The N was from NH3 and corn silks. The biomass-derived catalyst exhibited a remarkably higher ORR activity, superior stability and tolerance to methanol poisoning effects in alkaline media than Pt/C catalyst. The catalyst also showed higher voltage and higher specific capacity than the Pt/C in a zinc–air battery and it may be an alternative to Pt/C in the practical application of the zinc–air battery. This study showed the possibility for rational design and preparation of high-performance electrocatalysts with a low-cost from a highly available and recyclable plant biomass.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...