Capillarity-induced directed self-assembly of patchy hexagram particles at the air–water interface†
Abstract
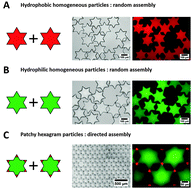
Directed self-assembly can produce ordered or organized superstructures from pre-existing building blocks through pre-programmed interactions. Encoding desired information into building blocks with specific directionality and strength, however, poses a significant challenge for the development of self-assembled superstructures. Here, we demonstrate that controlling the shape and patchiness of particles trapped at the air–water interface can represent a powerful approach for forming ordered macroscopic complex structures through capillary interactions. We designed hexagram particles using a micromolding method that allowed for precise control over the shape and, more importantly, the chemical patchiness of the particles. The assembly behaviors of these hexagram particles at the air–water interface were strongly affected by chemical patchiness. In particular, two-dimensional millimeter-scale ordered structures could be formed by varying the patchiness of the hexagram particles, and we attribute this effect to the delicate balance between the attractive and repulsive interactions among the patchy hexagram particles. Our results provide important clues for encoding information into patchy particles to achieve macroscopic assemblies via a simple molding technique and potentially pave a new pathway for the programmable assembly of particles at the air–water interface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...