Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling optimization enabled by automated feedback†
Abstract
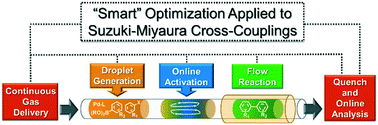
An automated, droplet-flow microfluidic system explores and optimizes Pd-catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. A smart optimal DoE-based algorithm is implemented to increase the turnover number and yield of the catalytic system considering both discrete variables—palladacycle and ligand—and continuous variables—temperature, time, and loading—simultaneously. The use of feedback allows for experiments to be run with catalysts and under conditions more likely to produce an optimum; consequently complex reaction optimizations are completed within 96 experiments. Response surfaces predicting reaction performance near the optima are generated and validated. From the screening results, shared attributes of successful precatalysts are identified, leading to improved understanding of the influence of ligand selection upon transmetalation and oxidative addition in the reaction mechanism. Dialkylbiarylphosphine, trialkylphosphine, and bidentate ligands are assessed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...