Magnetic Ni/PPy nanocomposite as effective reusable adsorbent for removal of arsenite and fluoride from contaminated water†
Abstract
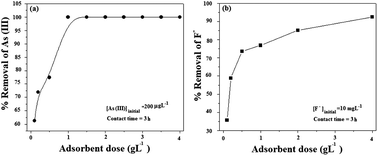
Magnetic nickel/polypyrrole (Ni/PPy) nanostructures have been synthesized at room temperature via an in situ oxidative polymerization of pyrrole (Py) monomers in the presence of FeCl3 oxidant in an aqueous suspension of Ni nanoflowers and characterized by XRD, FESEM, TEM, FTIR and Raman methods. Room temperature magnetic measurement shows that the magnetic properties of Ni are retained in all the nanocomposites. Ni/PPy nanostructures exhibit excellent adsorption efficiency in the removal of arsenic and fluoride from contaminated water as well as in the real ground water of Assam, India. Interestingly, Ni can be magnetically separated below its WHO prescribed toxicity value. The equilibrium data have been tested based on the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models. It is also found that the nanocomposite after adsorption could be regenerated by treating with acid/alkali and easily separated from the reaction mixture by the application of a magnetic field.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...