Hydropathy: the controlling factor behind the inhibition of Aβ fibrillation by graphene oxide†
Abstract
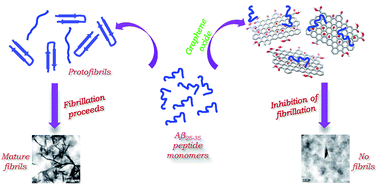
Protein and peptide aggregation/fibrillation is reported to be responsible for several neurological disorders. Fibrillation of the amyloid β-peptide fragment (25–35) which is a biologically active region of the full length peptide, has been observed to be significantly inhibited in presence of the two dimensional nanomaterial graphene oxide (GO). Fibrillation and inhibition of the Aβ25–35 peptide by GO has been performed at 37 °C at physiological pH (pH 7.4). The inhibition process is monitored by ThioflavinT fluorescence (ThT), circular dichroism spectroscopy, matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry, dynamic light scattering experiments etc. The soluble fraction of the protein is quantified by the BCA assay. Microscopic techniques are used to study the morphology of the fibrils formed. GO is observed to inhibit the fibrillation even at very low concentrations and is amplified with increase in concentration of GO. ThT kinetic data fitted well with a sigmoidal curve and shows that GO is able to lengthen the lag phase of the fibrillation process. It appears that surface adsorption of protein on the nanomaterial prevents the monomers to come together. It is speculated that the presence of both polar and non-polar moieties in GO interact strongly with the hydrophobic and hydrophilic residues of the Aβ25–35 peptide monomer units, thus preventing further aggregation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...